6 Reasons Why A Car's RPM Aren't Steady
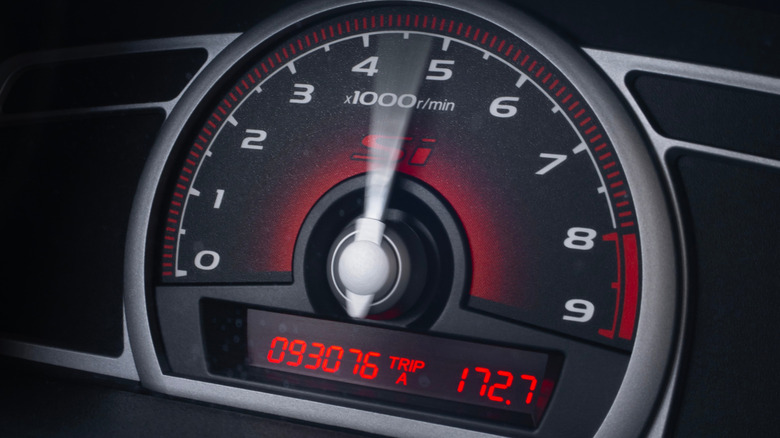
In an internal combustion engine, combustion cycles make the pistons move in a controlled way and activate a chain of mechanical parts that turns the crankshaft. That last part is what indirectly moves the vehicle's wheels on the ground, after going through the transmission system to be reduced and make the final power delivery safe. In cars, the crankshaft's movement is measured by the tachometer as revolutions per minute (rpm), usually expressed by the thousands.
Normally, the engine's rpm follows the power demand set by the driver in a linear way: it shows minimal variation when the car is idling and steadily increases as the gas pedal is further pressed until the point where, in most transmissions, it's necessary to activate a higher gear — though this point is highly variable according to the car. When the rpm behave erratically, with noticeable ups and downs while idling and/or that aren't consistent with the driver's pressure on the gas pedal, it's usually the sign of a problem.
The most common causes for fluctuating rpm can be listed as follows: clogged injectors, a faulty pump, and/or low-quality fuel may be affecting fuel supply; leaking hoses, dirty filters, and/or a problematic idle control valve may be affecting the air flow; malfunctioning sensors may be forcing the engine to run with incorrect combustion parameters; and a leaking and/or slipping transmission may be throwing the rpm off balance.
Problems related to the combustion cycle are the most common
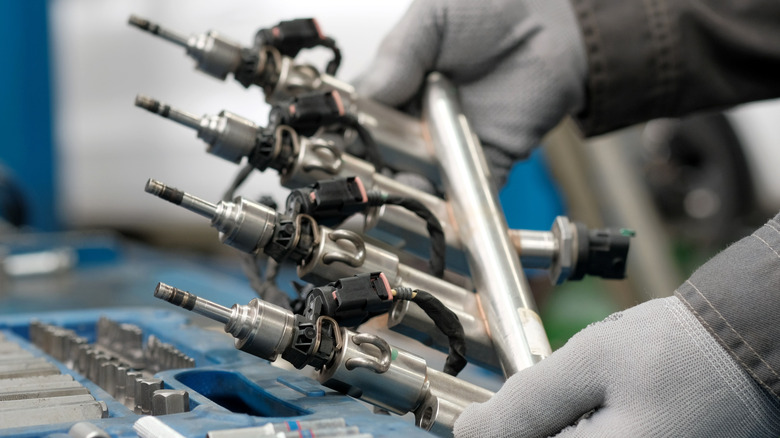
Reason #1: Fuel supply. Over time, injectors and filter get dirty with particles that come from the engine's regular operation and may become clogged. The fuel pump, in turn, may work less well as time passes, since it has a limited life. When any of those issues happen, those parts stop following the parameters set by the electronic control unit (ECU) for efficient combustion and make the fuel supply lower than usual. Besides fluctuating rpm, the car may suffer power loss in unexpected moments as well as higher fuel consumption.
Reason #2: Air supply. Air filters become dirty over time and may get clogged. However, the problem may also come from a damaged and/or loose vacuum hose toward the cylinders, a leaking manifold gasket, and/or a faulty idle air control valve. In all those cases, the air flow becomes different from expected, the engine stops following the ECU (not much differently from the case above), and the rpm may end up rising or dropping unpredictably when driving at low speeds.
Reason #3: Ignition system. If the spark plugs, spark plug wires, or ignition coils are worn out, they will no longer keep up with the timing of the combustion cycles in the engine's cylinders. That issue may cause detonation or pre-ignition, but either way it will also lead to irregular behavior when accelerating and, once again, fluctuating rpm when idling.
Sensors and transmission can cause problems, too
Reason #4: Mass airflow sensor. This sensor measures how much air enters the cylinders and sends that data to the ECU, which adjusts the fuel ratio to send an efficient air/fuel mixture to the cylinders. Issues with this sensor, such as incorrect readings, are another potential cause of combustion cycles being executed improperly and, as a consequence, engine rpm fluctuating.
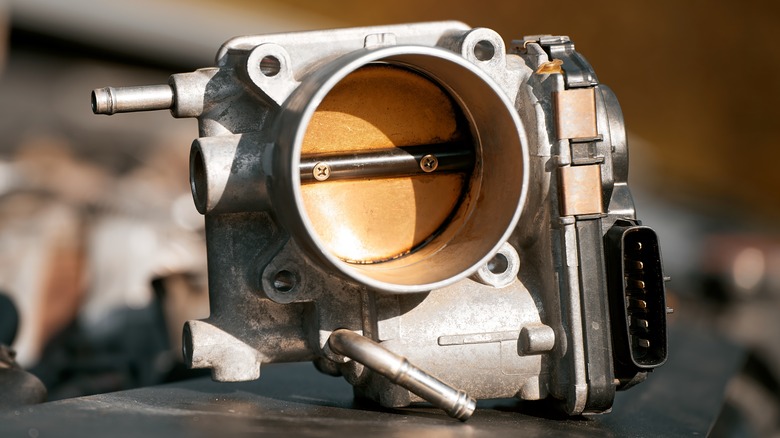
Reason #5: Throttle position sensor. Modern cars use this sensor to detect how hard the driver is pressing the gas pedal and send that data to the ECU, where it's converted into a signal that determines how much the throttle body needs to open. If this sensor malfunctions, the car ends up accelerating differently, less and/or more slowly than expected, and with the rpm varying in an unpredictable way.
Reason #6: Transmission fluid. If the system has a leak and the fluid level drops, the transmission might begin to slip. The spin reduction between the crankshaft and the wheels becomes irregular and leads to several other issues: The car may experience delayed gear shifting (even if its transmission is automatic), softer resistance on the clutch pedal (in manual cars), and fluctuating and/or higher than usual rpm when idling or accelerating.