The Pros & Cons Of 4-Cylinder Engines
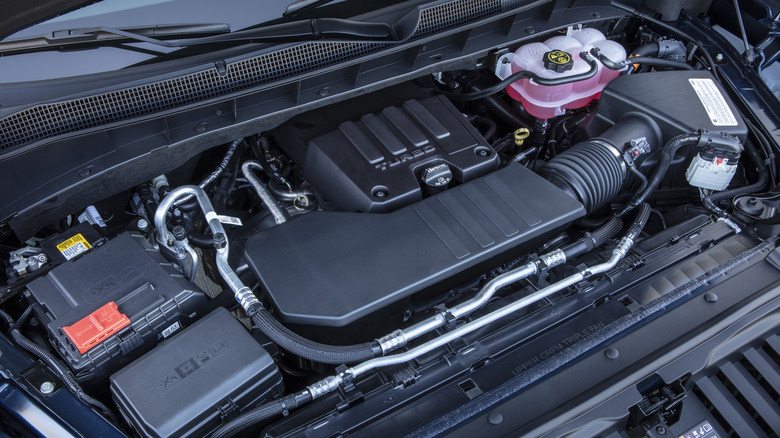
Four-cylinder engines have been part of the automotive scene for over a century. Yet the quest for more power under the hood dominated most of the 20th century, giving rise to six- and eight-cylinder power plants, with smaller engines often relegated to base-model duty. However, today's market is shifting as four-cylinder engines, beefed up with turbochargers, increasingly push aside V6s and V8s. The reason comes down to efficiency: fewer cylinders mean better fuel economy, and when combined with growing regulatory pressure and stricter emissions targets, the four-cylinder's resurgence becomes easy to understand.
The newly tubocharged 2023 Toyota Highlander is a good example. The automaker replaced its long-serving 3.5-liter V6 with a 2.4-liter four-cylinder that produces 265 horsepower and 310 pound-feet of torque. While horsepower dropped by 30 ponies, torque output increased by 17% over the V6. In announcing the changeover, Toyota didn't hide its motivations: better fuel economy and reduced emissions.
Chevrolet followed a similar path with the revamped 2024 Traverse midsize SUV. The previous generation's 3.6-liter V6 engine was dropped in favor of a turbocharged 2.5-liter inline-4. However, Chevy managed to increase horsepower and torque — 328 hp and 326 lb-ft compared with 310 hp and 266 lb-ft from the outgoing V6 — showing that downsizing doesn't always mean giving up performance.
Advantages of four-cylinder engines
Efficiency is the hallmark of four-cylinders. Smaller displacement and a simpler design translate into engines that burn less fuel and produce fewer emissions. Add modern turbocharging to the mix, and power loss becomes almost a non-issue. Car and Driver recorded a 0-60 time of 6.7 seconds for a V6-equipped 2022 Highlander, while the 2023 four-cylinder version reached the mark in 7.2 seconds. Meanwhile, EPA-estimated combined fuel economy for those same model years rose from 23 mpg to 25 mpg. Reduced emissions are another positive byproduct. Toyota reported that the engine switch with Highlander cut nitrous oxide output in half.
Lightweight design is another advantage of four-cylinder power plants. These engines have fewer moving parts and a smaller footprint, which can reduce vehicle weight and improve handling. A 2025 Ford Mustang EcoBoost with a turbocharged 2.3-liter four-cylinder weighs 3,588 pounds, while the V8-equipped Mustang GT tips the scales at 3,832 pounds. In a 2021 review of the previous-generation Mustang, comedian and car collector Jay Leno had good things to say about its four-cylinder edition on "Jay Leno's Garage": "I loved it better than the V8 because in the hills, it really handled lighter. I mean, I was stunned at how — what a nice driving car it was."
High-pressure direct injection, variable valve timing, and low-friction internal coatings make modern fours smoother and more responsive than their predecessors. Automakers have tuned these power plants to deliver more mid-range torque, so acceleration is less of a chore. Forced induction has also helped Mazda engineers reduce turbo lag in the company's SkyActiv engine family.
Disadvantages of four-cylinder engines
While four-cylinder engines have come a long way over the decades, they're not perfect, even with modern improvements. One drawback centers on refinement issues. Because a four-cylinder fires less frequently per crankshaft rotation, these engines can feel less smooth than larger ones. A V6 or V8 has more overlapping power strokes that produce more even crankshaft turns. An Edmunds review of the 2023 Highlander calls out how much noisier the cabin is with four-cylinder power compared to the V6, especially when the engine speed reaches 3,000 rpm.
Another downside can involve towing. While the engine switch didn't affect the Highlander's 5,000-pound tow rating, it can matter with other vehicles. The 2025 Chevrolet Silverado 1500 equipped with a turbocharged 2.7-liter four-cylinder can tow up to about 9,200 pounds, while the same truck fitted with the 6.2-liter V8 and an optional tow package increases capacity to roughly 13,300 pounds. When equipped with the base turbocharged 2.0-liter four-cylinder engine, the Cadillac XT6 can tow 1,000 pounds, but the same vehicle equipped with a 3.6-liter V6 has a trailering capacity of 4,000 pounds.
Other disadvantages are less quantifiable: maintenance and reliability. To deliver big-engine torque, turbo-fours require high boost pressure, which adds heat. There's also the mechanical complexity of turbochargers, intercoolers, and extra plumbing, creating additional potential trouble spots over naturally aspirated engines. And turbo engines require more frequent oil changes. While no metric points to a four-cylinder engine being less dependable or more costly to own, logic says that more parts don't help keep repair bills to a minimum. Turbocharged engines, regardless of cylinder count, are no strangers to problems.